From context-aware:to knowledge-aware Boosting OOV tokens recognition in slot tagging with background knowledge
摘要
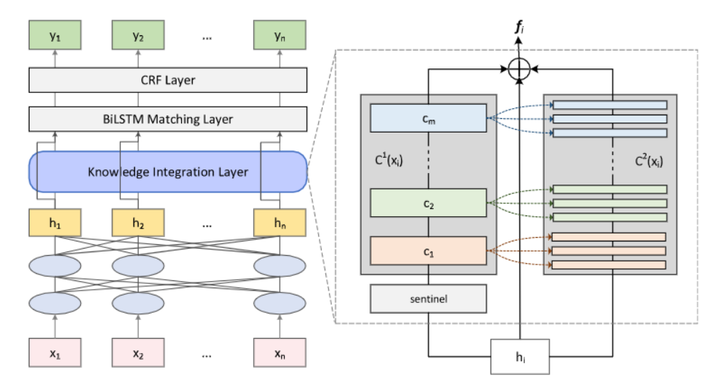
Neural-based context-aware models for slot tagging tasks in language understanding have achieved state-of-the-art performance, especially deep contextualized models, such as ELMo, BERT. However, the presence of out-of-vocab (OOV) words significantly degrades the performance of neural-based models, especially in a few-shot scenario. In this paper, we propose a novel knowledge-aware slot tagging model to integrate contextual representation of input text and the large-scale lexical background knowledge. Besides, we use multi-level graph attention to explicitly reason via lexical relations. We aim to leverage both linguistic regularities covered by deep language models (LM) and high-quality background knowledge derived from curated knowledge bases (KB). Consequently, our model could infer rare and unseen words in the test dataset by incorporating contextual semantics learned from the training dataset and lexical relations from ontology. The experiments show that our proposed knowledge integration mechanism achieves consistent improvements across settings with different sizes of training data on two public benchmark datasets. We also show through detailed analysis that incorporating background knowledge effectively alleviates issues of data scarcity.